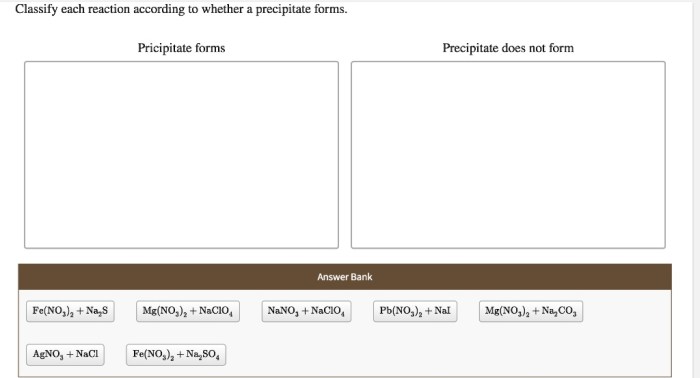
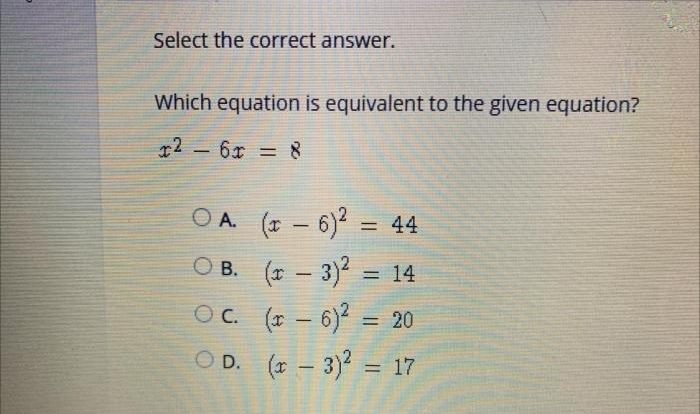
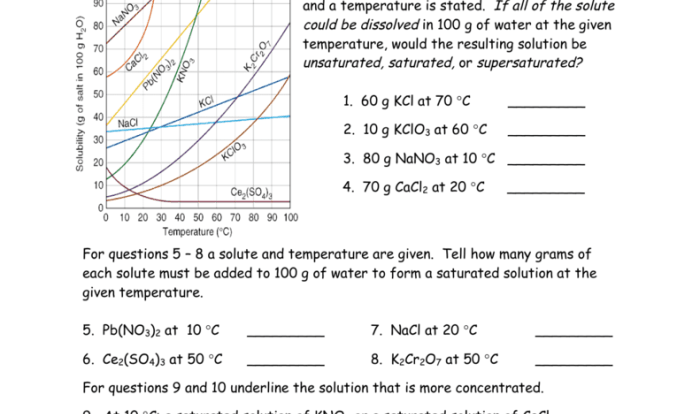
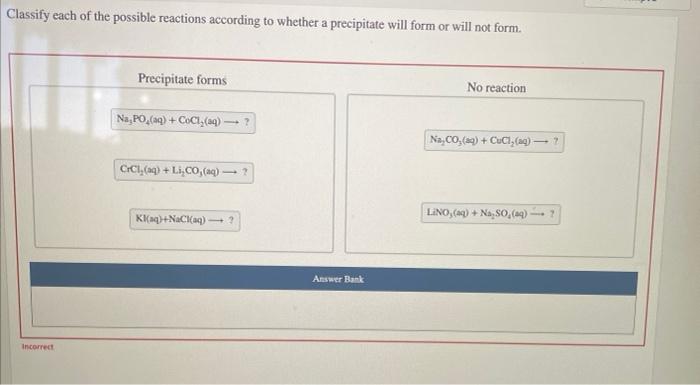
Classify each reaction according to whether a precipitate forms, delving into the fascinating world of chemical reactions and their unique characteristics. This exploration unveils the intricacies of precipitation, a fundamental concept that shapes the behavior of substances in solution.
Precipitation reactions, marked by the formation of an insoluble solid compound, play a crucial role in various scientific disciplines and industrial applications. Understanding the factors that influence precipitate formation empowers us to harness the power of these reactions for practical purposes.
Precipitation Reactions: Classify Each Reaction According To Whether A Precipitate Forms
A precipitate is a solid compound that forms when two solutions are mixed and the resulting compound is insoluble in the solvent. The formation of a precipitate is a common occurrence in chemistry and has a wide range of applications.
Types of Reactions
- Reactions that form precipitates:These reactions involve the mixing of two solutions that contain ions that combine to form an insoluble compound. For example, the reaction between silver nitrate (AgNO 3) and sodium chloride (NaCl) forms a precipitate of silver chloride (AgCl).
- Reactions that do not form precipitates:These reactions involve the mixing of two solutions that contain ions that do not combine to form an insoluble compound. For example, the reaction between sodium chloride (NaCl) and potassium chloride (KCl) does not form a precipitate because both compounds are soluble in water.
Factors Affecting Precipitation, Classify each reaction according to whether a precipitate forms
The formation of a precipitate is influenced by several factors, including:
- Concentration:The concentration of the reactants affects the rate of precipitation. The higher the concentration of the reactants, the faster the precipitate will form.
- Temperature:The temperature of the reaction affects the solubility of the reactants. The higher the temperature, the more soluble the reactants will be and the less likely a precipitate will form.
- Solubility:The solubility of the product affects whether a precipitate will form. If the product is insoluble, it will precipitate out of solution. If the product is soluble, it will remain in solution.
Identifying Precipitates
Precipitates can be identified by their physical characteristics, which include:
- Appearance:Precipitates are typically solids that are cloudy or opaque.
- Texture:Precipitates can be crystalline or amorphous.
- Solubility:Precipitates are insoluble in the solvent.
Applications of Precipitation Reactions
Precipitation reactions have a wide range of applications, including:
- Water treatment:Precipitation reactions are used to remove impurities from water. For example, the addition of lime (CaO) to water causes the formation of a precipitate of calcium carbonate (CaCO 3), which removes suspended solids from the water.
- Chemical analysis:Precipitation reactions are used to identify and quantify ions in solution. For example, the addition of silver nitrate (AgNO 3) to a solution of chloride ions (Cl –) causes the formation of a precipitate of silver chloride (AgCl), which can be used to determine the concentration of chloride ions in the solution.
- Industrial processes:Precipitation reactions are used in a variety of industrial processes, such as the production of paper, textiles, and pharmaceuticals.
User Queries
What is the definition of a precipitate in a chemical reaction?
A precipitate is an insoluble solid compound that forms when two solutions are mixed, resulting in the combination of ions to create a new substance with reduced solubility.
How can we identify a precipitate in a reaction?
Precipitates are typically characterized by their cloudiness or turbidity, indicating the presence of suspended solid particles in the solution. They can also be identified by their distinct color or texture.