Which of the following statements about demand curves is true? This question delves into the fundamental concepts of demand curves, exploring their types, determinants, and applications. Understanding demand curves is crucial for businesses and economists alike, as they provide valuable insights into consumer behavior and market dynamics.
Demand curves graphically represent the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity demanded by consumers. They play a pivotal role in determining market equilibrium and serve as a tool for forecasting future demand. This article will delve into the intricacies of demand curves, examining the factors that influence their shape and position, and highlighting their practical applications.
Demand Curves: Basic Concepts: Which Of The Following Statements About Demand Curves Is True
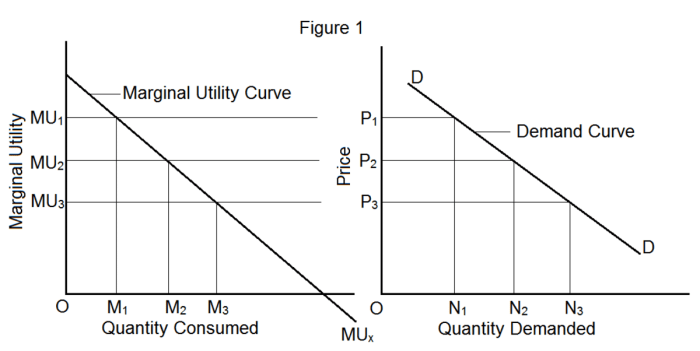
Demand curves are graphical representations of the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity demanded by consumers. They illustrate the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded, meaning that as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa.
Demand curves play a crucial role in understanding market dynamics and are essential for businesses to make informed decisions regarding pricing, production, and marketing strategies.
Types of Demand Curves
Demand curves can be classified into different types based on their shape and slope:
- Linear Demand Curve:A straight line that represents a constant change in quantity demanded for each unit change in price.
- Non-Linear Demand Curve:A curved line that represents a varying change in quantity demanded for each unit change in price.
- Elastic Demand Curve:A curve that shows a relatively large change in quantity demanded for a small change in price.
- Inelastic Demand Curve:A curve that shows a relatively small change in quantity demanded for a large change in price.
The shape and slope of a demand curve are influenced by various factors, including consumer preferences, availability of substitutes, income levels, and expectations about future prices.
Determinants of Demand
The position and movement of demand curves are determined by several key factors:
- Price of the Good or Service:The most direct determinant of demand, affecting quantity demanded in an inverse relationship.
- Income of Consumers:Higher incomes typically lead to increased demand for normal goods and decreased demand for inferior goods.
- Prices of Related Goods:Substitute goods have a positive relationship with demand, while complementary goods have a negative relationship.
- Consumer Tastes and Preferences:Changes in consumer preferences can shift demand curves.
- Expectations:Beliefs about future prices or availability can influence current demand.
Market Equilibrium
Market equilibrium occurs when the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded at a particular price. Demand curves play a vital role in determining this equilibrium point, as they represent the quantity demanded at different prices.
In a competitive market, market equilibrium is achieved through the interaction of supply and demand forces. When the price is above equilibrium, there is a surplus (excess supply), and sellers will lower prices to attract buyers. Conversely, when the price is below equilibrium, there is a shortage (excess demand), and sellers will raise prices to discourage buyers.
Applications of Demand Curves, Which of the following statements about demand curves is true
Demand curves have numerous applications in business decision-making:
- Pricing Strategy:Businesses use demand curves to determine optimal pricing strategies that maximize revenue.
- Production Planning:Demand curves help businesses forecast demand and plan production levels to meet consumer needs.
- Marketing Campaigns:Businesses use demand curves to evaluate the impact of marketing campaigns on consumer demand.
- Demand Forecasting:Demand curves can be used to predict future demand based on historical data and market trends.
Essential FAQs
What is the law of demand?
The law of demand states that, all other factors being equal, as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa.
What is an elastic demand curve?
An elastic demand curve is a curve where the percentage change in quantity demanded is greater than the percentage change in price. This means that consumers are very responsive to price changes.
What is an inelastic demand curve?
An inelastic demand curve is a curve where the percentage change in quantity demanded is less than the percentage change in price. This means that consumers are not very responsive to price changes.