Welcome to the Metrics and Measurements Answer Key, your definitive guide to understanding and utilizing metrics and measurements effectively. In this comprehensive resource, we delve into the intricacies of data analysis, empowering you with the knowledge and tools to make informed decisions and drive success.
Metrics and measurements are the foundation of data-driven decision-making, providing valuable insights into performance, progress, and areas for improvement. This answer key provides a comprehensive overview of the different types of metrics and measurements, methods for collecting and analyzing data, and best practices for using metrics wisely.
Types of Metrics and Measurements
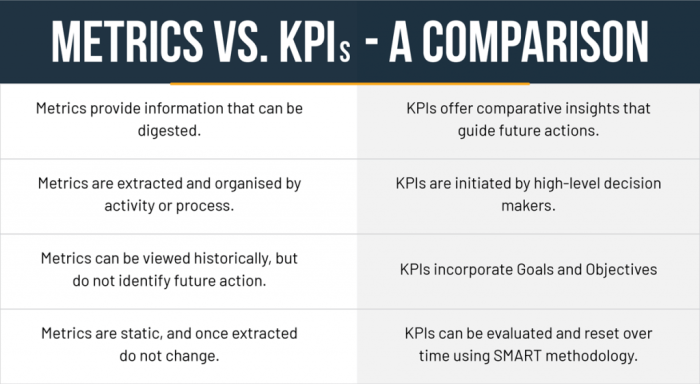
In various fields, metrics and measurements are essential tools for quantifying, evaluating, and tracking performance, progress, and outcomes. These metrics and measurements come in different types, each serving specific purposes and providing valuable insights.
The table below Artikels the different types of metrics and measurements, their definitions, and examples:
| Type | Definition | Examples | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quantitative | Measurements expressed in numerical values | Revenue, sales volume, website traffic | Financial performance, customer engagement, website effectiveness |
| Qualitative | Measurements expressed in non-numerical terms | Customer satisfaction, employee morale, brand reputation | Customer feedback, employee surveys, social media monitoring |
| Operational | Measurements related to daily operations | Production output, inventory levels, delivery time | Process efficiency, resource utilization, supply chain management |
| Financial | Measurements related to financial performance | Profitability, return on investment, cash flow | Business profitability, investment decisions, financial planning |
| Performance | Measurements related to individual or team performance | Sales targets, project completion rate, customer acquisition cost | Performance evaluation, goal setting, resource allocation |
| Process | Measurements related to business processes | Cycle time, error rate, customer satisfaction | Process improvement, quality control, customer experience management |
| Benchmarking | Measurements comparing performance against industry standards or competitors | Industry average sales, competitor market share | Identify areas for improvement, set realistic goals, stay competitive |
Methods for Collecting Metrics and Measurements
The choice of method for collecting metrics and measurements depends on the specific metrics being collected, the available resources, and the desired level of accuracy.
Common methods for collecting metrics and measurements include:
Surveys
- Surveys are a widely used method for collecting data from a large number of people.
- They can be administered online, by mail, or in person.
- Surveys can be used to collect both quantitative and qualitative data.
- However, surveys can be time-consuming to design and administer, and they may not always be accurate, as respondents may not always provide truthful or complete information.
Interviews
- Interviews are a more in-depth method of data collection than surveys.
- They allow the researcher to ask follow-up questions and probe for more detailed information.
- However, interviews can be time-consuming and expensive to conduct, and they may not be appropriate for large-scale data collection.
Observations
- Observations involve directly observing and recording the behavior of people or animals.
- This method can be used to collect data on a wide range of topics, such as customer behavior, animal behavior, or traffic patterns.
- However, observations can be time-consuming and may not always be accurate, as the observer may not be able to see everything that is happening.
Experiments
- Experiments are a controlled method of data collection that involves manipulating one or more independent variables to measure the effect on a dependent variable.
- This method can be used to test hypotheses and determine cause-and-effect relationships.
- However, experiments can be time-consuming and expensive to conduct, and they may not always be possible in real-world settings.
Document Analysis
- Document analysis involves collecting and analyzing written documents, such as reports, emails, or social media posts.
- This method can be used to collect data on a wide range of topics, such as customer feedback, employee performance, or organizational culture.
- However, document analysis can be time-consuming, and it may not always be possible to obtain all of the relevant documents.
Tools and Technologies for Analyzing Metrics and Measurements
To effectively analyze metrics and measurements, various tools and technologies are available. These tools offer a range of capabilities and limitations, catering to specific data analysis needs.
Open-Source Tools
Open-source tools provide cost-effective solutions for data analysis. They offer flexibility and customization options, allowing users to tailor the tools to their specific requirements.
- Python Pandas:A powerful data manipulation and analysis library with extensive functionality for data cleaning, transformation, and visualization.
- R:A statistical programming language and environment widely used for data analysis, modeling, and visualization.
Commercial Software
Commercial software offers comprehensive features and dedicated support, often catering to specific industry or business needs.
- Tableau:A leading data visualization and analytics platform with a user-friendly interface and advanced data exploration capabilities.
- Power BI:A cloud-based business intelligence platform from Microsoft, offering interactive dashboards, data modeling, and machine learning integration.
Cloud-Based Services
Cloud-based services provide scalable and accessible data analysis solutions without the need for local infrastructure.
- Google Analytics:A comprehensive web analytics platform that provides insights into website traffic, user behavior, and marketing campaigns.
- AWS QuickSight:A fully managed business intelligence service from Amazon Web Services, offering interactive visualizations and machine learning-powered insights.
Comparison Table
The following table compares the key features, benefits, and pricing of the aforementioned tools and technologies:
| Tool/Technology | Features | Benefits | Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Python Pandas | Data manipulation, transformation, visualization | Open-source, customizable | Free |
| R | Statistical programming, modeling, visualization | Open-source, extensive statistical functions | Free |
| Tableau | Data visualization, interactive dashboards | User-friendly interface, advanced analytics | Paid, subscription-based |
| Power BI | Business intelligence, data modeling, machine learning | Cloud-based, integrated with Microsoft ecosystem | Paid, subscription-based |
| Google Analytics | Web analytics, user behavior tracking | Free, widely adopted | Freemium, paid for advanced features |
| AWS QuickSight | Business intelligence, machine learning insights | Fully managed, scalable | Paid, usage-based pricing |
Best Practices for Using Metrics and Measurements
To ensure effective utilization of metrics and measurements, it is imperative to establish clear goals and objectives. These serve as the foundation for selecting appropriate metrics, guiding data collection efforts, and interpreting results. Without well-defined goals, it becomes challenging to determine the relevance and significance of the metrics being tracked.
Guidelines for Using Metrics and Measurements Wisely
- Set clear goals and objectives:Define the specific outcomes or improvements you aim to achieve by using metrics and measurements.
- Select relevant metrics:Choose metrics that directly align with your goals and provide meaningful insights into your performance.
- Establish baselines and targets:Determine a starting point for your measurements and set realistic targets for improvement.
- Collect data consistently:Ensure data is collected regularly and in a standardized manner to maintain accuracy and reliability.
- Analyze data regularly:Schedule regular intervals to review and analyze the collected data, identifying trends and areas for improvement.
- Communicate results effectively:Share the findings of your analysis with stakeholders in a clear and actionable manner.
- Use metrics to drive decision-making:Utilize the insights gained from metrics to inform decision-making processes and optimize performance.
- Review and refine:Regularly assess the effectiveness of your metrics and measurements and make adjustments as needed to ensure continued relevance and accuracy.
Case Studies of Effective Metrics and Measurements
Metrics and measurements have become essential tools for organizations seeking to improve their performance. By tracking and analyzing key metrics, businesses can identify areas for improvement, set realistic goals, and make data-driven decisions.
Numerous organizations have successfully used metrics and measurements to enhance their operations and achieve significant results. The following table presents case studies of companies that have effectively implemented metrics and measurements:
| Organization | Industry | Metrics Used | Results Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | Website traffic, conversion rates, customer satisfaction | Improved website performance, increased revenue, enhanced customer experience | |
| Amazon | Retail | Sales volume, customer reviews, inventory levels | Optimized product offerings, improved customer loyalty, reduced operating costs |
| Starbucks | Food and Beverage | Customer satisfaction, employee turnover, store profitability | Increased customer loyalty, reduced employee turnover, improved store performance |
| Nike | Apparel and Footwear | Sales revenue, brand awareness, customer engagement | Grew market share, enhanced brand reputation, increased customer engagement |
| Walmart | Retail | Inventory levels, supply chain efficiency, customer satisfaction | Reduced inventory costs, improved supply chain management, enhanced customer satisfaction |
These case studies demonstrate the power of metrics and measurements in driving organizational success. By carefully selecting and tracking relevant metrics, businesses can gain valuable insights into their operations and make informed decisions that lead to improved performance.
Future Trends in Metrics and Measurements: Metrics And Measurements Answer Key
The field of metrics and measurements is constantly evolving, with new technologies and methodologies emerging that are shaping the future of data analysis. These trends are driven by the increasing availability of data, the need for more sophisticated analysis techniques, and the desire to make better use of data to improve decision-making.
Some of the key trends in metrics and measurements include:
The Use of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- AI is being used to automate many tasks in the data analysis process, such as data collection, cleaning, and analysis.
- This can free up data analysts to focus on more complex tasks, such as developing new metrics and measurements and interpreting the results of data analysis.
The Rise of Big Data
- The amount of data available to businesses is growing exponentially, and this is making it increasingly difficult to manage and analyze data effectively.
- New technologies, such as cloud computing and data lakes, are making it possible to store and process large amounts of data.
The Need for More Sophisticated Analysis Techniques
- As the amount of data available increases, so too does the need for more sophisticated analysis techniques.
- Traditional data analysis techniques are no longer sufficient to handle the complexity of big data.
The Importance of Data Visualization, Metrics and measurements answer key
- Data visualization is an important way to communicate the results of data analysis to decision-makers.
- New data visualization tools are making it easier to create clear and concise visualizations that can be easily understood by non-technical audiences.
The Need for Data Governance
- As the amount of data available increases, so too does the need for data governance.
- Data governance is the process of managing data in a way that ensures its accuracy, consistency, and security.
These are just a few of the key trends that are shaping the future of metrics and measurements. As these trends continue to evolve, it is important for businesses to stay up-to-date on the latest technologies and methodologies in order to remain competitive.
FAQ Overview
What are the different types of metrics and measurements?
Metrics and measurements encompass a wide range of types, including quantitative metrics (e.g., revenue, customer satisfaction), qualitative metrics (e.g., customer feedback, employee engagement), and operational metrics (e.g., production output, inventory levels).
How do I choose the right metrics and measurements for my business?
Selecting the appropriate metrics and measurements depends on your specific business goals and objectives. It’s crucial to align your metrics with your strategic priorities and ensure they provide meaningful insights into your performance.
What are the best practices for using metrics and measurements effectively?
Effective use of metrics and measurements involves setting clear goals, establishing a data collection plan, analyzing data regularly, and communicating insights effectively to stakeholders.